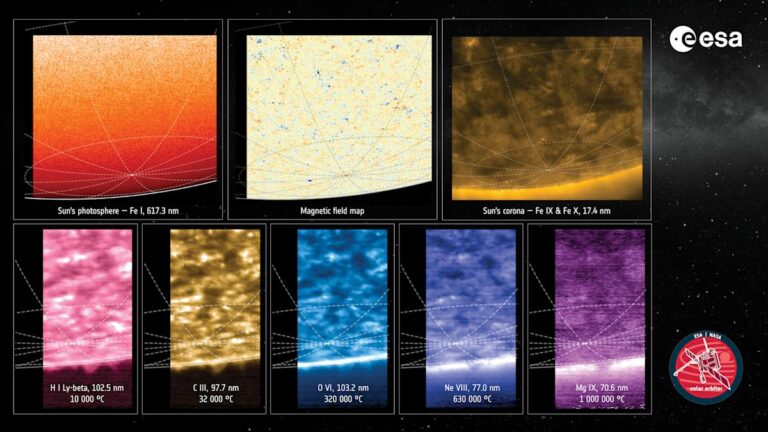
The Solar Orbiter has been observing the sun since 2021, but it surely just lately went on a facet journey to Venus which considerably tilted its orbit and gave it a superb view of the solar’s polar area. That’s the way it was capable of seize pictures that can traditionally be referred to as humankind’s first-ever views of the solar’s pole. All our galaxy’s planets and the opposite spacecraft we have deployed orbit the solar round an imaginary ecliptic aircraft alongside the star’s equator. However due to the Photo voltaic Orbiter’s Venus flyby, it now has a view of the solar from under its equator, permitting it to see the star’s southern pole clearly. The photographs you see above had been captured from an angle of 15 levels under the equator on March 16 and 17, however the probe has reached the 17 diploma most angle it may obtain since then.
Three of the probe’s devices had been accountable for the photographs. The Polarimetric and Helioseismic Imager (PHI) imaged the solar in seen gentle and mapped its floor magnetic discipline. In the meantime, the Excessive Ultraviolet Imager (EUI) imaged the solar in ultraviolet gentle, and the Spectral Imaging of the Coronal Atmosphere (SPICE) instrument captured gentle “coming from totally different temperatures of charged fuel above the solar’s floor, thereby revealing totally different layers of the solar’s environment.”
So what precisely was the Photo voltaic Orbiter capable of observe on the solar’s southern pole? Effectively, the pole’s magnetic discipline, merely put, is a multitude in the mean time. See, the solar’s magnetic discipline flips roughly each 11 years, and it is about to flip this yr if it hasn’t but. Usually, a magnet has a transparent north and south pole, however the orbiter’s PHI instrument confirmed that each north and south polarity magnetic fields are current on the solar’s south pole proper now. “This occurs just for a short while throughout every photo voltaic cycle, at photo voltaic most, when the Solar’s magnetic discipline flips and is at its most lively,” ESA defined.
After the flip, the magnetic discipline fixes itself in order that the poles have single polarities. The method is gradual, nonetheless, and it’ll take 5 to 6 years to realize photo voltaic minimal, whereby which the solar’s magnetic discipline is at its most orderly. These photo voltaic cycles or common magnetic discipline flips aren’t absolutely understood but, and the orbiter’s observations may very well be the important thing to unlocking that data.
As well as, scientists used the orbiter’s SPICE instrument to take Doppler measurements, or how briskly clumps of photo voltaic materials are shifting. They then took that data to create a velocity map that exhibits how photo voltaic materials strikes inside a particular layer of the solar. These measurements can present how the solar flings out particles into house within the type of solar winds, which is likely one of the orbiter’s key objectives.