Mars’s marred floor consists of craters, canyons, and mysterious formations that trace at a fancy geological previous. Scientists not too long ago studied a tantalizing function that might make clear the planet’s elusive historical past.
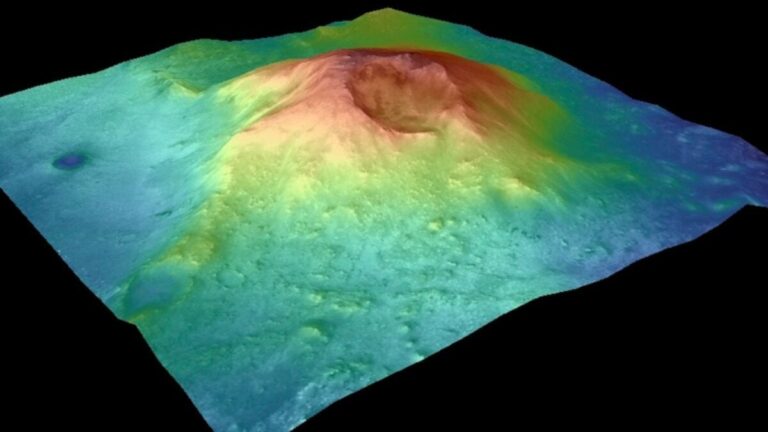
A mountain perched on the rim of Mars’ Jezero Crater may very well be a volcano hiding in plain sight, in response to a brand new research. This peak, referred to as Jezero Mons, may supply new perception into the Purple Planet’s geologic historical past and the potential for ancient Martian life, the researchers say.
The findings, revealed within the journal Communications Earth & Environment in Could, validate long-held suspicions that Jezero Mons is volcanic. Utilizing knowledge from three Mars orbiters and NASA’s Perseverance rover, researchers discovered placing similarities between this mountain and explosive volcanoes beforehand recognized on Mars and Earth.
“Jezero Crater is among the finest studied websites on Mars. If we’re simply now figuring out a volcano right here, think about what number of extra could possibly be on Mars,” said corresponding writer James Wray, a professor of astrogeology and distant sensing at Georgia Tech, in a college assertion. “Volcanoes could also be much more widespread throughout Mars than we thought.”
Wray has had a hunch that Jezero Mons is a volcano ever since he first laid eyes on it in 2007. “I used to be low-resolution photographs of the world and seen a mountain on the crater’s rim,” he recalled within the assertion. “To me, it seemed like a volcano, however it was tough to get further photos.” On the time, scientists had solely not too long ago found the Jezero crater. As soon as scientists decided that it was likely an ancient lake bed, imaging efforts targeted on its water historical past on the facet reverse Jezero Mons.
Then, shortly after NASA’s Perseverance rover landed in Jezero Crater in 2021, there was a break within the case. This rover gathers samples from the Martian surface to assist the seek for previous life, examine the planet’s local weather and geology, and pave the way in which for human exploration of the Purple Planet. Earlier than lengthy, knowledge from Perseverance confirmed that the crater’s ground was not sedimentary, as one would anticipate from a previously-flooded space. It was truly made of volcanic rock.
Wray puzzled if this igneous rock may have come from Jezero Mons. He teamed up with lead writer Sara Cuevas-Quiñones—a graduate pupil at Brown College who was working with Wray as a part of a summer season undergraduate analysis program on the time—to attempt to reply this query.
Wray, Cuevas-Quiñones, and their colleagues used a mixture of knowledge from the Mars Odyssey Orbiter, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, ExoMars Hint Gasoline Orbiter, and the Perseverance rover to “puzzle this out,” Wray mentioned. This wealth of knowledge allowed the researchers to achieve a deeper understanding of Jezero Mons’ traits and evaluate it to different recognized volcanoes.
They discovered that the scale and form of this peak is much like Martian volcanoes equivalent to Zephyria and Apollinarus Tholi, in addition to Mount Sidley in Antarctica. What’s extra, the researchers decided that the floor of Jezero Mons lacks affect craters and doesn’t retain warmth effectively—two indicators that it could be lined in volcanic ash. Components of the height’s northwestern flank additionally resembled edges of previous lava flows that seem to succeed in the crater ground, which may clarify why Perseverance discovered igneous rock there.
Whereas this doesn’t definitively show that Jezero Mons is a volcano, it’s a number of the strongest proof specialists have thus far. The findings mark an intriguing improvement within the seek for life in Jezero Crater. A volcano positioned so near this historical lake may need generated hydrothermal exercise—a supply of power that might have sustained previous life.
Now, the researchers await the return of Perseverance’s samples. Radioisotope relationship can decide the exact age of the igneous rocks this rover collected, which may then be used to extra precisely estimate Jezero Crater’s age, in response to the researchers. This could supply helpful insights into the geological historical past of the Purple Planet.
At the moment, NASA and its worldwide companions don’t have any stable plan to get this assortment of rocks and dirt again to Earth, however the company is reviewing two Mars Pattern Return (MSR) mission methods with a purpose of confirming this system in 2026. President Donald Trump’s 2026 price range proposal, nonetheless, threatens to derail this program. If handed by Congress, the price range would terminate the MSR mission on the grounds that it’s “grossly over price range” and its objectives might be achieved by human missions to Mars.
Wray is hopeful that he’ll get his arms on Perseverance’s finds a method or one other. “If these samples are returned to Earth, we are able to do unbelievable, groundbreaking science with them,” he mentioned.