There might not but be telescopes able to unlocking all of the secrets and techniques of supermassive black holes, however AI is now on the case. Just lately, a world staff of astronomers efficiently educated a neural community with tens of millions of black gap simulations to permit it to interpret fuzzy information captured from these enigmatic house objects in actual life.
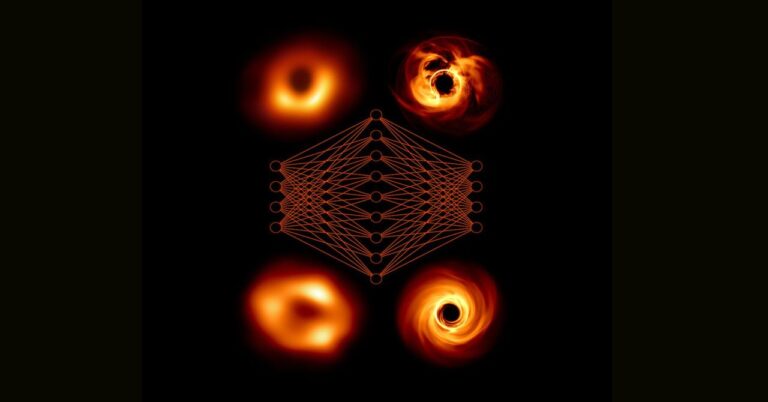
Of the varied strategies for investigating a black gap, the Occasion Horizon Telescope is probably the most well-known. The EHT isn’t a single instrument however somewhat quite a lot of radio telescopes world wide that work collectively like a single telescope. Due to the EHT, it’s been attainable to acquire pictures of the supermassive black holes M87 and Sagittarius A*. These aren’t pictures within the conventional sense however as a substitute are visualizations of radio waves coming from the black holes.
To create these pictures, supercomputers in numerous components of the world processed the radio indicators captured by the EHT. However within the course of, they discarded a lot of the data gathered, because it was troublesome to interpret. The brand new neural community, educated by specialists on the Morgridge Analysis Institute in Wisconsin, goals to faucet into that sea of information to enhance the decision of the EHT’s readings and make new discoveries.
In accordance with a press launch from the institute, the unreal intelligence efficiently analyzed the once-discarded info and established new parameters of Sagittarius A*, which sits on the middle of the Milky Manner. An alternate picture of the black gap’s construction was generated, with this revealing some new traits of the black gap.
“Researchers now suspect that the black gap on the middle of the Milky Manner is spinning at nearly high velocity,” wrote the researchers in a press release. The brand new picture additionally additionally signifies that the black gap’s rotation axis factors to the Earth and offers clues as to the causes and traits of the disks of fabric that flow into across the black gap.
Astronomers had beforehand estimated that Sagittarius A* rotates at a average to quick velocity. Realizing its precise rotational velocity is essential, because it permits us to deduce how the radiation across the black gap behaves and offers clues about its stability.
“That we’re defying the prevailing idea is after all thrilling,” lead researcher Michael Janssen, of Radboud College Nijmegen within the Netherlands, stated within the press launch. “Nevertheless, I see our AI and machine studying strategy primarily as a primary step. Subsequent, we are going to enhance and lengthen the related fashions and simulations.”
This story initially appeared on WIRED en Español and has been translated from Spanish.